

Take a look at the following table in order to understand the construction of the curve. Your outputs might also take the form of research and development time, or internal investment. Alternatively, it might be measured in terms of the number of hours labour you can provide for a project. In this case, the output might be measured in terms of the number of clients or customers you can provide with a service. If you have a service business, or create digital products, things get a little bit trickier. Again, when you create simple physical products, this is pretty self explanatory. That is, this is the quantity of your products which you can actually create. Outputs are much simpler to get your head around. Instead, they rely entirely on intangible resources. Similarly, some products, like mobile apps or web development projects don’t actually require raw materials.

Logistics to bring your products to market.įor example, you might have all of the raw materials in the world, but not enough machinery to combine them into a final product.The trickier thing is intangible resources.Īn intangible resource is something which you need to create your products, which you can’t actually hold in your hands. Naturally, on the one hand this includes raw materials, packaging and any other physical goods you might need to actually create the product itself. Resources are anything which is needed to make your products. A table of supposed quantities that your operation can produce is sketched onto the graph.Each axis has the quantity of one of the common products,.Now, let us identify how a production possibilities curve is constructed: It is important to know which of your products to prioritize over another one.įor a growing company, that is an incredible loss. Likewise, Buying too much material while not outputting all of it into a sell-able product is considered to be a waste of money that could otherwise be used on something else. In order to allocate resources to one production, it must be removed from another. To understand the production possibilities curve, you must consider the opportunity cost.Īccording to the concept of scarcity, your business only has a limited amount of resources that must be utilized to create your outputs.
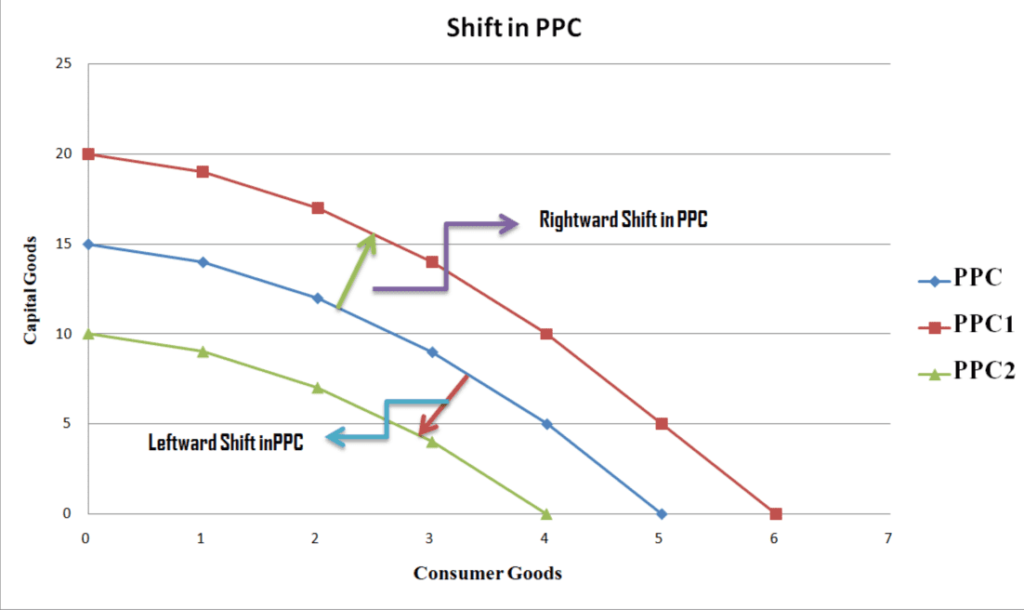
It shows the maximum amount output that is possible for both products which you can then compare to your actual output to ensure that there are no inefficiencies occurring. The definition of production possibilities curve is a graphical representation combining two products that share common resources in your operation. What is a Production Possibilities Curve? Now, in order to begin, let us understand the production possibilities curve. Naturally, this means that you maximize your output (and profits) while minimizing unused resources which might otherwise go to waste.

Ensuring that your operation is working at maximum efficiency means that you are utilizing all your resources. It is a measure of the efficiency of your current operation regarding the available resources and the amount of two products produced. Today we will be discussing the production possibilities curve which allows you to compare two products that share common resources in order to balance the amount of each. It is generally a good idea to use multiple graphs in order to have a clear overview of your various products. When it comes to production, there are several graphical representations that allow you to balance between the products you produce. This allows you to identify problems and recognize any potential improvements. It allows you to accurately analyse its productivity. A production possibilities curve is crucial for keeping track of your business.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
